What is Fission?
Nuclear fission is a reaction in which the nucleus of a heavy atom splits into two or more smaller nuclei and releases energy while doing so. Said differently, a large unstable atom (a uranium atom off crystalized on the rock of the earth) can break apart and release energy. Typically, this is the result of a free neutron smashing into the nucleus of a fissionable atom (like uranium-235) and causing that nucleus to split. When it splits, it gives off energy (primarily as heat) and a few more neutrons in the process. These new neutrons can then impact and split other neighboring uranium atoms, sometimes triggering additional fission events. Very quickly, we have a chain reaction, a self-sustaining series of splits. Each split is releasing additional neutrons and heat in tiny fractions of a second.
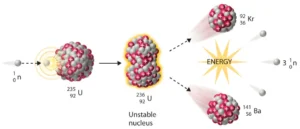
Benefits:
- It produces a huge amount of energy from a very small amount of fuel.
- Fission power plants do not emit greenhouse gases during operation.
- Nuclear power plants provide reliable electricity. They can run continuously for long periods and aren’t dependent on weather conditions, unlike solar or wind
What is fusion?
Nuclear fusion is the opposite of nuclear fission, instead of splitting a large atom, fusion combines two small atoms into one, releasing a huge amount of energy as a result of mass turning into energy. This is the same process that powers the Sun and stars. In the Sun’s core, hydrogen atoms fuse into helium, producing the sunlight and warmth we experience on Earth. However, making fusion happen isn’t easy. Since atomic nuclei are positively charged and naturally repel each other, extremely high temperatures and pressure are needed to force them close enough to fuse. While the Sun’s core is around 15 million °C, scientists on Earth must reach even higher temperatures, over 100 million °C, because we don’t have the Sun’s intense gravity. Fusion fuel is incredibly efficient; just a few grams can produce as much energy as burning tons of coal.
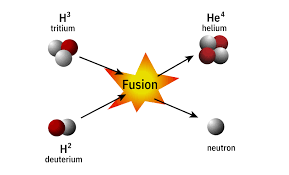
Benefits:
- Fusion power could run for millions of years without running out of fuel
- Fusion does not produce the long-lived radioactive waste that fission does.
- A fusion reactor cannot run away or explode like a fission reactor potentially could.
- Fusion produces energy without burning fuel in air, so it emits no carbon dioxide or other greenhouse gases while generating power